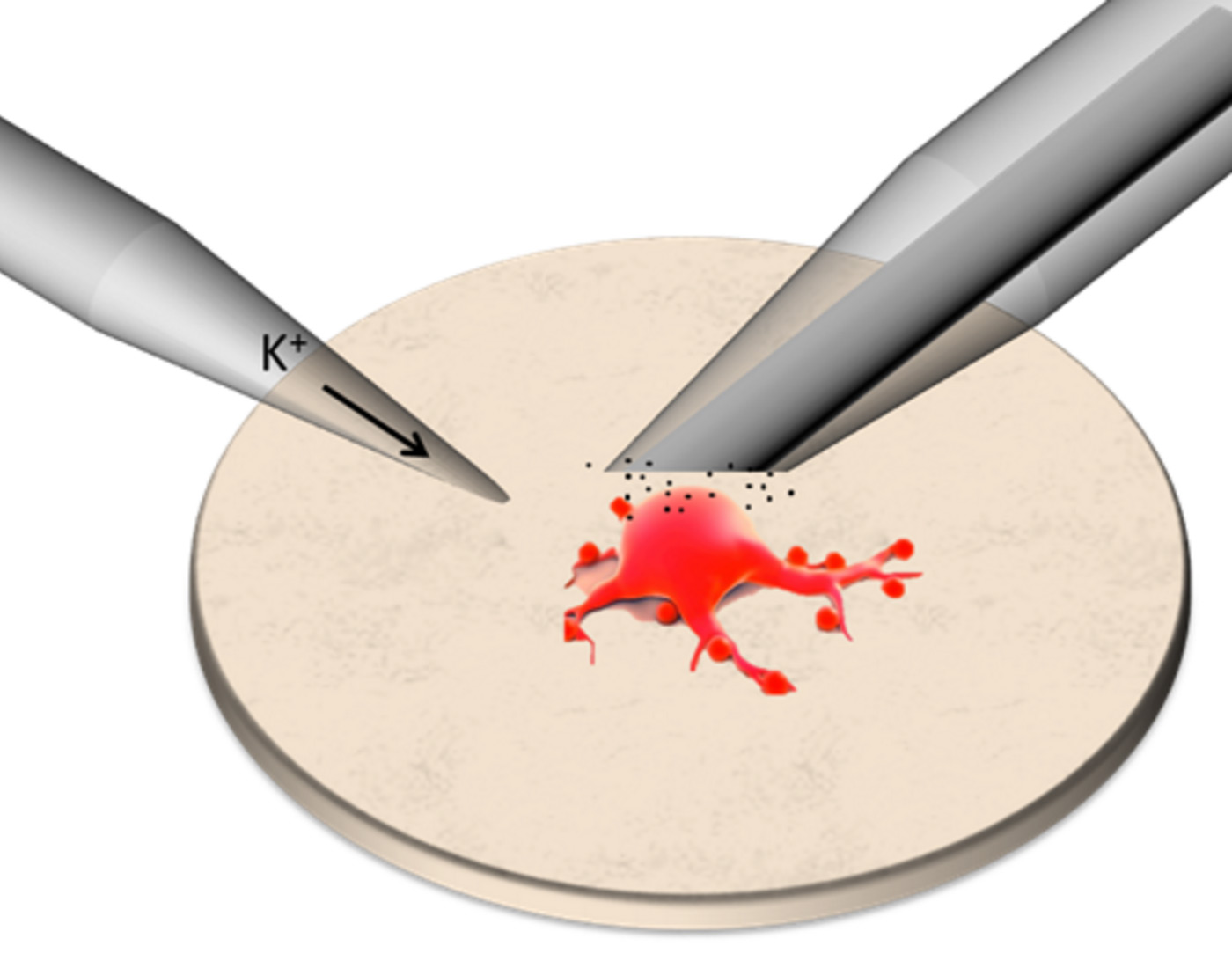
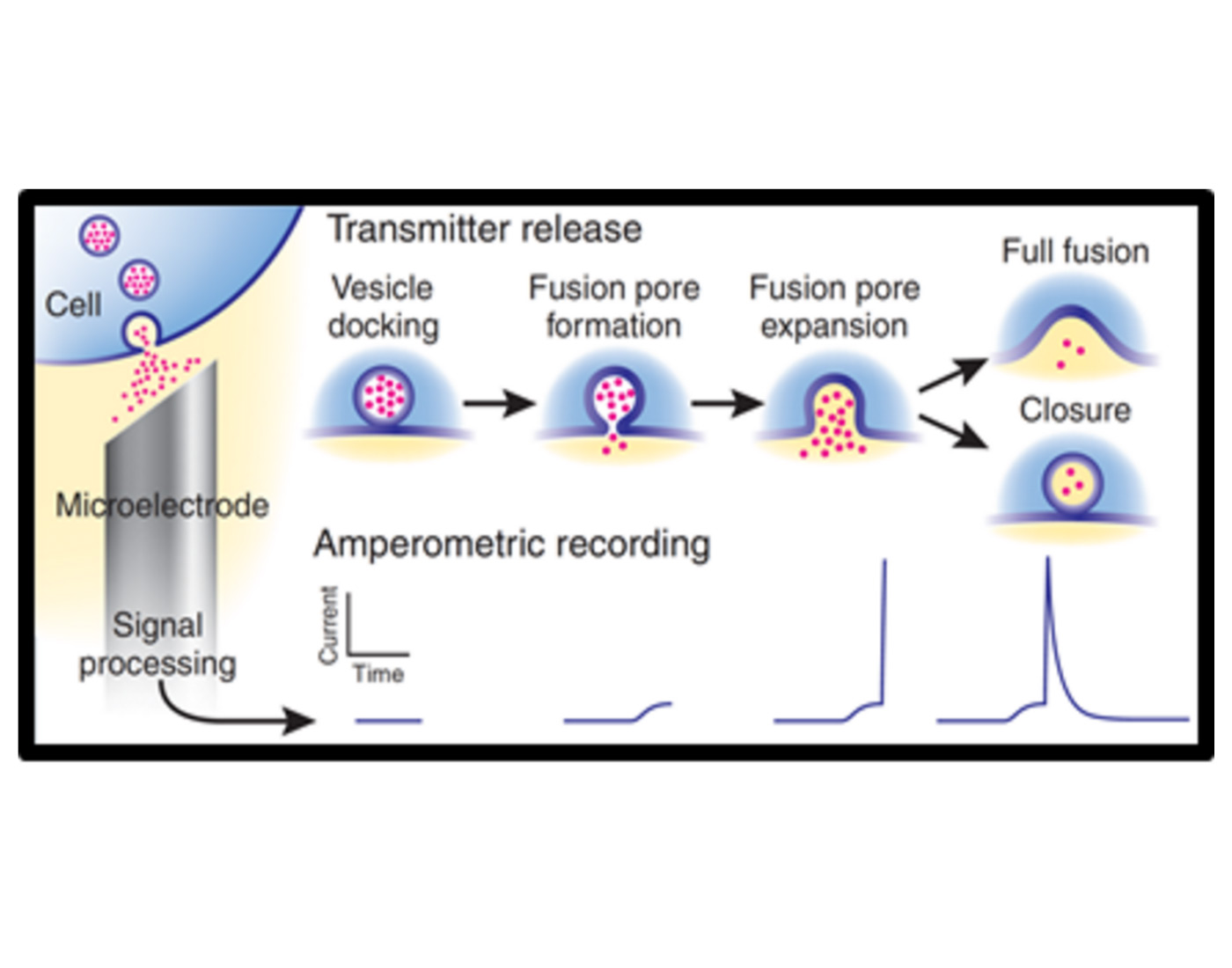
An electrode is positioned on top of a single cell to create an artificial synapse.
The potential at the electrode is held at 800 mV, and the passage of current monitored.
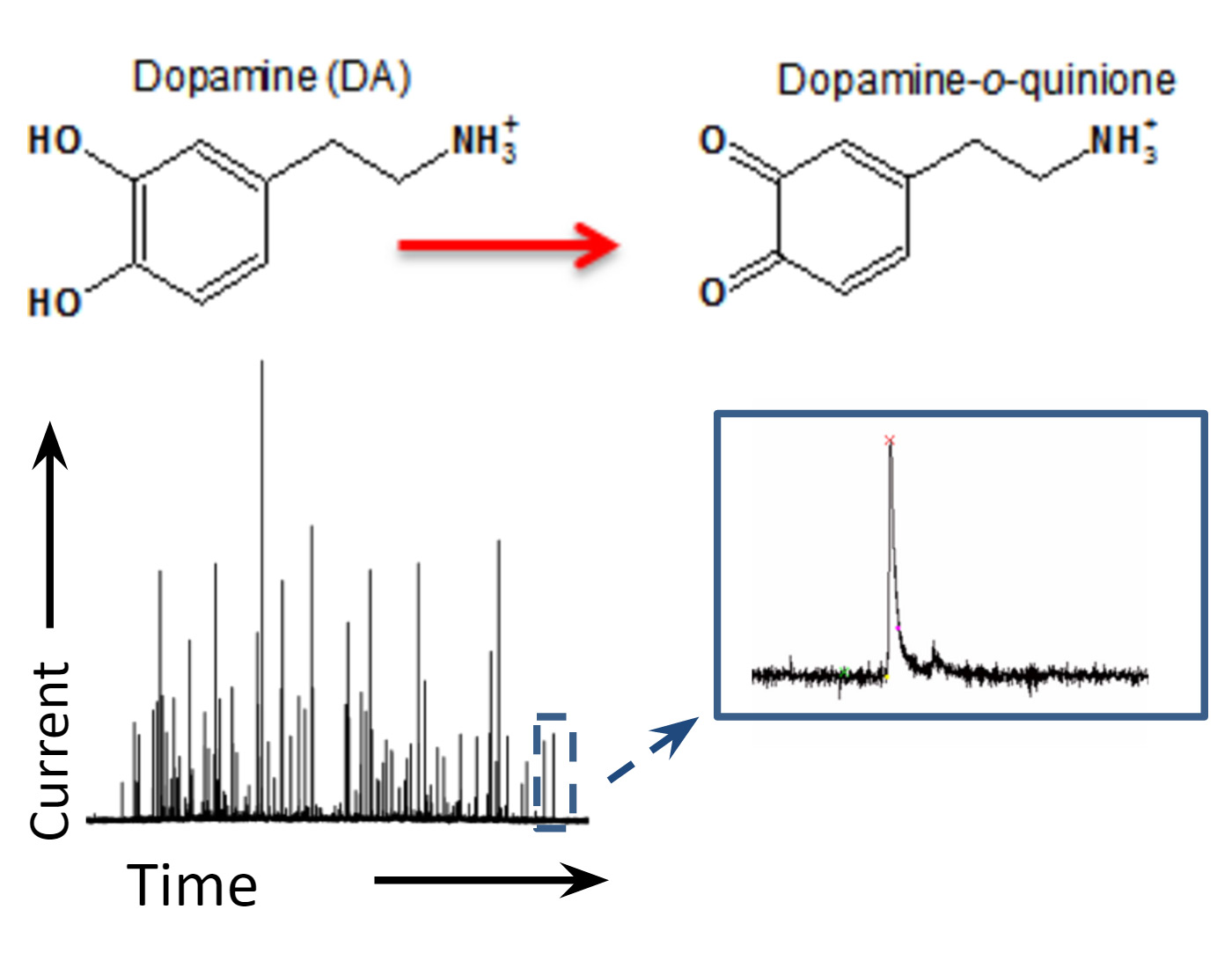
Upon exocytosis, dopamine and other catecholamines (including norepinephrine, epinephrine) are oxidized, yielding characteristic peaks when plotting current vs. time.
Each peak represents a single vesicle fusing to the cell membrane.